Labral Repair
What is the labrum and what does it do?
The labrum in the shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral joint, is a rubbery ring of fibrocartilage that surrounds the socket side of the joint.
The labrum has several functions:
- Deepens the shallow socket of the shoulder joint, which helps to increase what is structurally a very instable joint
- Serves as a point of attachment for the biceps tendon, as well as the glenohumeral ligaments (which are part of the joint capsule and help to stabilize the joint);
- Acts as a chock-block to resist translation of the ball portion of the joint
How does a labral tear occur?
Labral tears can occur in a variety of ways. Some common causes are:
- Traumatic dislocation of the shoulder
- Fall onto an outstretched hand
- Direct blow to the shoulder
- Football tackle when the arm is forcibly moved back and out
- Heavy lifting
What does a labral tear feel like?
A labral tear can manifest itself in a variety of ways. Not every patient has the same symptoms. The type of symptoms you have can depend on the location and severity of the tear.
Common complaints from labral tears are:
- Pain localized deep in the shoulder;
- Painful popping or clicking deep in the shoulder;
- Catching with specific motions;
- A sensation that the shoulder is sliding in and out of place;
- Pain that radiates from the shoulder down the biceps muscle
How is a labral tear diagnosed?
Your MD or PA will make this diagnosis using a combination of several things:
- History: You may remember a specific incident that caused your pain or recall when your pain suddenly increased;
- Exam: We will perform several tests to assess pain, range of motion, and stability of the shoulder;
- Radiographs: X-rays will be taken to check for any other cause of your pain;
- MRA: An MRI with dye injected into the joint will be ordered if a tear is suspected. The dye allows us to visualize the integrity of the labral tissue.
How are labral tears treated?
While conservative treatment consisting of physical therapy and/or anti-inflammatory medications may be appropriate for some patients, most patients will require surgical intervention for their labral tear.
What occurs during surgery?
Most surgery for labral tears can be performed arthroscopically.
The procedure will vary depending on the size and location of the tear.
Some tears can be shaved down to stable tissue using a small arthroscopic shaver, while others require that we place a small screw type of anchor into the bone of the socket and physically stitch the labrum back down to its proper location.
The Patient is positioned on their side and the doctor is working inside the joint, while watching the procedure on the monitor to the right.
During the surgery, we may also find that the biceps tendon attachment is very damaged and it needs to be detached and transferred to a new location.
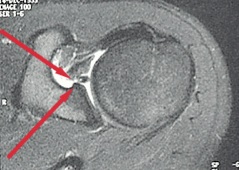
MRI arthrogram with red arrows pointing to tear of the labrum
What to expect after surgery?
After surgery you will spend between one week and four weeks in a sling. It is very important that you use the sling exactly as you have been instructed. This will allow your labrum to heal properly.
- You will have a dressing over the shoulder that can be removed after 48 hours and you may shower at that time.
- When you shower, please make sure you do not disturb the paper strips covering the incisions and ensure that you thoroughly pat your incisions dry when you are finished.
- At your first postoperative visit, you will be instructed when you can remove your sling. You will also be instructed when you may resume driving.
- You will be provided with a prescription to attend physical therapy. Your physical therapist will guide you through an exercise program designed to help you gain range of motion and strength